In order to understand the terms and definitions of the heating and cooling industry, it’s important to first have a basic idea of the refrigeration cycle and its principles… if you have questions or concerns about your system, Integrity Air in Jasper, Georgia can help. Call (706) 889-6092.
 Principles of Refrigeration
Principles of Refrigeration
– Liquids absorb heat when changed from liquid to gas
– Gases give off heat when changed from gas to liquid
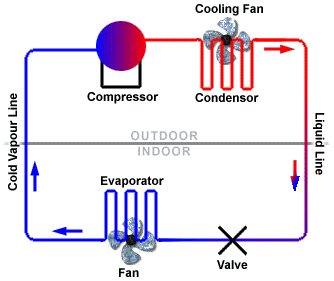
All air conditioners use the same cycle of compression, condensation, expansion, and evaporation in a closed system.
- The refrigerant comes into the compressor as a low-pressure gas, it is compressed and then moves out of the compressor as a high-pressure gas.
- The gas then flows to the condenser. Here the gas condenses to a liquid, and gives off its heat to the outside air.
- The liquid then moves to the expansion valve under high pressure. This valve restricts the flow of fluid and lowers its pressure as it leaves the valve.
- The low-pressure liquid moves to the evaporator where heat from the inside air is absorbed and changes it from a liquid to a gas.
- As a hot low-pressure gas, the refrigerant moves to the compressor where the entire cycle is repeated.

Glossary of HVAC Terms
Air Conditioner
An appliance, system, or mechanism designed to dehumidify and extract heat from an area. Usually this term is reserved for smaller self contained units such as a residential system.
Air flow
The quantity of air the system moves measured in cubic feet per minute (cfm) for each ton of AC capacity.
Air Handler
The central indoor unit consisting of a blower/fan and the evaporator (summer)/condenser (winter) coil. This does not include the ductwork.
Coil
Located inside the blower compartment or air handler, the evaporator coil holds the chilled refrigerant that the compressor moves into it. As the air from the blower fan moves over the coil, the cold refrigerant removes the heat from your home’s air. The refrigerant becomes warmer and travels to the condenser coil outdoors. See also Condenser.
With a heat pump, the process reverses in the winter and the evaporator coil expels heat from the refrigerant into your home, instead of absorbing it and taking it outdoors. Most heat pumps have auxiliary heating elements that are part of the evaporator coil components to supply heat when temperatures fall below a certain point. See also Heat Pump.
Compressor
The outside part of your AC – the condensing unit which raises the temperature and pressure of the refrigerant.
Condenser
A component in the basic refrigeration cycle that removes heat from the system. The condenser is the hot side of an air conditioner or heat pump. See also Coil.
Dehumidifier
The equipment that extracts and removes humidity from the air.
Evaporator
A component in the basic refrigeration cycle that absorbs or adds heat to the system. Evaporators can be used to absorb heat from air or from a liquid. The evaporator is the cold side of an air conditioner or heat pump. See also Heat Pump.
Filter
The air filter prevents contaminants from entering the equipment and must be maintained or replaced regularly. A central heating and cooling system may use multiple filters including a filter in the refrigeration system which removes dirt and particles from the system.
Furnace
A component of an HVAC system that adds heat to air or an intermediate fluid by burning fuel (typically natural gas, oil, or propane) in a heat exchanger.
Heat Pump
A compressor that cycles hot or cold air in the opposite direction… In summer, it moves heat from inside to outside; in winter, it moves heat from outside to inside. See also Coil.
HVAC
Stands for heating, ventilating, and air conditioning and is pronounced either (H-V-A-C) or (H-Vac). Either works!
Load Calculation
As part of the HVAC design or selection process, load calculation is determining how much heat a house gains or loses due to various factors.
Return
The side of the duct system that pulls air from the house back to the air handler to be conditioned again.
SEER
SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) is a rating of the cooling output during a typical cooling-season divided by the total electric energy input during the same period. Higher SEER rating = more energy efficient.
Thermostat
The HVAC component which monitors temperature and performs actions to maintain it near a desired setpoint.
Tons
Not the weight of the air conditioner but the capacity. One ton of air conditioning capacity is equal to 12,000 BTU/hour.
Zoning
A system of sectioning a building into zones which are controlled independently of each other. Temperature is controlled by different thermostats.

In Summary
Being equipped with common air conditioning and heating terms is helpful when dealing with HVAC issues around the home and should make the homeowner feel more confident when discussing heating and cooling with a professional. Brandon and the team at Integrity Air are experienced with heating and cooling systems in the North Georgia area including Cherokee, Pickens and Gilmer counties. Contact us today!


